
Knowledge is power. Having the ability to be confident when discussing printing is a must for the print salesman. To provide a better understanding of the printing industry, we have compiled this glossary of terms that will help you learn about the terms and concepts used when discussing print projects. Although the primary focus of this glossary is carbonless business forms other print types are addressed. For more in depth explanations of business form printing concepts, visit our Forms Knowledge Base by Clicking Here
-
AC
Author's Correction
-
Abrasion Resistance
The resistance to scratching of a surface of paper by other paper surfaces or other materials.
-
Absorbency
The ability of a material to take up moisture
-
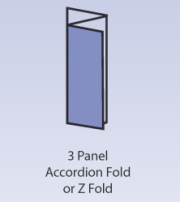 Accordion Fold
Accordion FoldA type of paper folding in which each fold runs in the opposite direction to the previous fold creating a pleated or accordion effect.
-
Achromatic
The non-colors... black, white and gray.
-
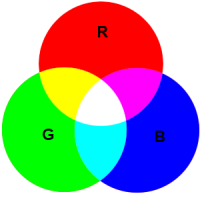 Additive Colors
Additive ColorsAdditive colors are created by the mixing of visible light that has been emitted from different color light sources. Red, Green and Blue (RGB)are mixed to produce different colors. Both computer monitors and televisions us additive color to represent images on their screens. RGB colors can only represent approximately 70% of visible colors. Because of the difference between additive and subtractive color (see below) it is difficult to tell what an item on the computer screen will actually look like in print because of the compressed color gamut used in printing.
-
Aerate
This refers to a manual process whereby an air stream is blown onto paper sheets to create a riffling effect that separates the sheets as they are fed to the printing press.
-
Agate
A typographical measurement unit equal to 5 1/2 points. Agate may also refer to type of the size of 5 1/2 points. It can be set a approximately 13 lines to the inch. This is the smallest readable font size for newsprint and is often used for statistical information or legal notices. In England it has the appellation of ruby.
-
Air
Large white areas in a design layout.
-
Alignment
The condition of type and or art materials as they level up on a horizontal or vertical line.
-
Alley
A term for a random, coincidental path or a row of white space within a segment of copy.
-
 Angle Bar
Angle BarOn web presses, the paper must be turned to allow for printing on the front and back. This is accomplished by the use of the turn bar. After the back has been printed paper is rotated on the press by running it through the turn bar. It is usually located just after the the last back print station.
-
Aniline
Oil-based solvent (quick drying) used in the preparation process of dyes and inks. Can be used in security inks to bleed color into the paper resulting in a visible indication that the document is an original.
-
Anodized Plate
In lithography, a plate manufactured with a barrier of aluminum oxide, which prevents chemical reactions that break down the plate; it provides optimum press performance.
-
Apron
The white area of text (or illustrations) at the margins which form a foldout.
-
Aqueous Plate
Water soluble plate coatings, which are less toxic and less polluting.
-
Arms
Those elements of letters that branch out from the stem of a letter, such as: "K" and "Y".
-
Art Work
Any materials or images that are prepared for graphic reproduction.
-
Artwork
All illustrated material, ornamentation, photos and charts etc., that is prepared for reproduction.
-
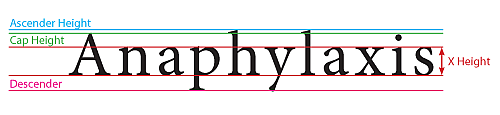 Ascender
AscenderAny part of a lower case letter which rises above the X-height of the font, such as "f", "l" and "h".
-
Author's Alterations (AA's)
Changes made after composition stage where customer is responsible for additional charges.
-
BF
An abbreviation for boldface, used to determine where boldface copy is to be used. Reference, boldface.
-
Back Gum
Adhesive which is applied to the back seams of an envelope to join them together. This may also be called seam gum.
-
 Back Printing
Back PrintingPrinting on the reverse side of a form or sheet of paper. On business forms this area is typically printed in a screened color (50% or less) or in light gray (e.g. PMS 423 Gray) in order to prevent the back image from showing through (bleeding) on the front. Thicker stocks and coated papers printing may be printed without screening. Business form backers are typically either head to head or tumble style. A tumble style backer is printed head down on the page. When the page is tumbled over, it is then in a readable position.
-
Back To Back
Print applied to both sides of a sheet of paper.
-
Backbone
That portion of the binding, which connects the front of the book with the back of the book; also called "back".
-
Background
That portion of a photograph or line art drawing that appears furthest from the eye; the surface upon which the main image is superimposed.
-
Balance
A term used to describe the aesthetic or harmony of elements, whether they are photos, art or copy, within a layout or design.
-
Balloon
In an illustration, any line which encircles copy, or dialogue.
-
Banding
Packaging of forms or envelopes by the placement of a paper band around a counted number of items. This is especially useful for items that are distributed in a set number to various individuals or locations.
-
Banker's Flap Envelope
Also called wallet flap; the wallet flap has more rounded flap edges.
-
Banner
The primary headline usually spanning the entire width of a page.
-
Barn Doors
A device with two sets of thin metal doors (horizontal and vertical) placed before a light source to control the direction of light.
-
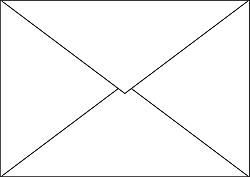 Baronial Envelope
Baronial EnvelopeEnvelope that is primarily used for formal announcements and greetings. This type of envelope has a large pointed flap and diagonal seams.
-
Bas Relief
A three dimensional impression is which the image stands just slightly out from the flat background. References, blind emboss.
-
Base Line
This is a term used to describe the imaginary horizontal line upon which stand capitals, lower case letters, punctuation points etc.
-
Basic Size
This term refers to a standard size of paper stock; even though the required size may be smaller or larger.
-
Basis Weight
Basis or basic weight refers to the weight, in pounds, of a ream (500 sheets) of paper cut to a given standard size for that particular paper grade.
24 Pound Bond - 17" x 22"
Writing Papers - 17" x 22"
Cover Weights - 20" x 26" -
Bauhaus
A design school in Germany where the Sans Serif font was originated. The school believed that "less is more" and that "form should follow function". The Bauhaus believed that beautiful and functional objects could be produced through the use of industrial processes. This of course stood in direct opposition to the Arts and Crafts movement.
-
Bindery
The department in a print shop that specializes in finishing the printed product. Their operations may include cutting, binding, folding, and drilling of the printed product.
-
Binding
Various methods of securing folded sections together and or fastening them to a cover, to form single copies of a book. The most common types of binding include saddle stitching, perfect binding, case binding, coil binding, wire o, and comb binding
-
Black Letter
An old style of typeface used in Germany in the 15th century, also referred to as Old English (US) and Gothic (UK).
-
Blanket
On offset presses a fabric-reinforced sheet of rubber to transfer the impression from the plate onto the paper.
-
Blanket To Blanket Press
A printing method in which there are two blanket cylinders through which a sheet of paper is passed and printed on both sides.
-
 Bleed
BleedExtra ink area that crosses trim line, used to allow for variations that occur when the reproduction is trimmed or die-cut. A typical bleed amount would be 1/8" or 1/4" on each side of the artwork when it is printed. This area is often required for the printing process to prevent extra trimming of the item being printed. Note that bleed is a specific amount of area. Am area of print that is slightly larger that the image is not considered a bleed. Also see "crop marks" entry for further illustration.
-
Blind Emboss
A design or bas relief impression that is made without using inks or metal foils.
-
Blind Folio
Page number not printed on page.
-
Blistering
Although seemingly dry, paper does contain approximately 5% moisture. In cases where there is excessive moisture, and the paper is passed through a high heat-drying chamber, the moisture within the paper actually boils and causes a bubble or blistering effect.
-
Block
Illustrations or line art etched onto zinc or copper plates and used in letterpress printing.
-
Blocking
The adhesion of one coated sheet to another, causing paper tears or particles of the coating to shed away from the paper surface.
-
 Blockout or Block out
Blockout or Block outA pattern that is printed to obscure the transfer of information on an area of a business form. This is often used to cover up information such as price, credit card number, or any other information that is not needed by the party receiving that copy of the form.
-
Blow-up
Any enlargement of photos, copies or line art.
-
Body
The main shank or portion of the letter character other than the ascenders and descenders. Also: A term used to define the thickness or viscosity of printer's ink.
-
Body Size
The point size of a particular type character.
-
Boiler Plate
Repetitive blocks of type that are picked up and included routinely without recreating them.
-
 Boldface
BoldfaceAny type that has a heavier black stroke that makes it more conspicuous. The image above shows 3 different weights of the typeface Myriad Pro.
-
Bolts
The edges of folded sheets of paper, which are trimmed off in the final stages of production.
-
Bond
A grade of strong, durable writing and printing paper that has a standard size of 17x22 inches. This is the primary type of paper used for business documents, letterhead, copies, and most basic printed documents.
-
Book
A general classification to describe papers used to print books; its standard size is 25x38 inches. A printed work which contains more than 64 pages.
-
Bounce
1. A registration problem, usually on copiers, where the image appears to bounce back and forth. A bounce usually occurs in one direction depending on how the paper is passing through the machine. This is usually accented by card stock (especially if it's over the machine's spec). 2. When a customer refuses a job for whatever reason.
-
Brace
A character " }" used to group lines, or phrases.
-
Bristol Board
A board paper of various thickness; having a smooth finish and used for printing and drawing.
-
Broad Fold
A term given to the fold whereby paper is folded with the short side running with the grain.
-
Brochure
A printed document whose chief purpose is to convey information about a product, service, company, organization, concept, event or individual to a target group. An example would be the brochures available in state welcome centers and tourist areas. The most common type of brochure is printed on both sides and folded into thirds. Some brochures, such as maps may be quite large and contain complex folds. Brochures can also consist of multiple pages bound into a booklet using saddle stitching or some form of gluing. Most brochures are printed in process color (CMYK) on glossy paper. Small quantities of a brochure may be printed digitally with offset presses being used for larger quantities and better pricing.
-
Buckle Folder
A portion of the binding machinery with rollers that fold the paper.
-
Bulk
A term used to define the number of pages per inch of a book relative to its given basis weight.
-
Bulk
A term given to paper to describe its thickness relative to its weight.
-
 Bullet
BulletA boldface square, dot or other symbol, used before a sentence to emphasize its importance.
-
Burn
A term used in plate making to describe the amount of plate exposure time.
-
CB - Coated Back
Coated back (CB) paper starts out as bond grade paper. It is coated with microencapsulated dye on the backside of the paper. This paper reacts to pressure, such as handwriting, by releasing dye from the microcapsules that react with the clay and resin on coated front (CF) paper to produce an image in the shape of the pressure applied.
Click Here for an extended article and links concerning carbonless paper. -
CF - Coated Front
Coated front (CF) paper starts out as bond grade paper. It is coated with resin and clay on the front side of the paper. This paper reacts with dye released by pressure from the coated back (CB) paper to produce an image in the shape of the pressure applied. Click Here for an extended article and links concerning carbonless paper.
-
CFB - Coated Front And Back
Coated front and back (CFB) paper starts out as bond grade paper. It is coated with resin and clay on the front side of the paper. This paper reacts with dye released by pressure from the coated back (CB) paper to produce an image in the shape of the pressure applied. It is also coated with microencapsulated dye on the backside of the paper which releases dye from the microcapsules that react with the clay and resin on coated front (CF) paper to produce an image. In a multipart set with more than 2 sheets CFB comprises all the parts except for the face and back. Click Here for an extended article and links concerning carbonless paper.
-
Calendar Rolls
A series of metal rolls at the end of a paper machine; when the paper is passed between these rolls it increases its smoothness and glossy surface.
-
Caliper
The measurement of thickness of paper expressed in thousandths of an inch or mils.
-
Callout
An area of type which has been set in larger or bolder type from the body copy for added emphasis. This area may consist of a single word or a phrase.
-
Camera Ready Copy
Copy that can be scanned or shot with a camera that reproduces a high quality copy of the original. Copy needs to smooth, clean and printed in a dark ink.. Forms with areas that are screened, have pantographs, areas of uneven ink or bleed through of the backer are not considered suitable candidates for camera ready copy. Also known as shootable copy. Due to advances in technology almost all camera copy is now scanned.
-
Cap Line
An imaginary horizontal line running across the tops of capital letters.
-
Caps & Lower Case
Instructions in the typesetting process that indicate the use of a capital letter to start a sentence and the rest of the letters in lower case.
-
 Caps & Small Caps
Caps & Small CapsTwo sizes of capital letters made in one size of type.
-
Caption
Copy placed near a photo or illustration that describes or identifies the image or the items that the image contains.
-
Carbon Black
A pigment made of elemental carbon and ash.
-
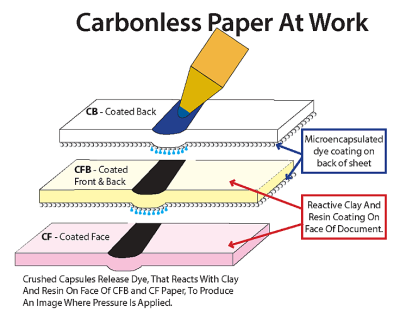 Carbonless Paper
Carbonless PaperCarbonless paper is used as an alternative to paper with carbon interleaves. Carbonless paper starts out as bond grade paper. It is coated with either microencapsulated dye or resin and clay. Paper designated as CB, or coated back, has been coated with a layer of micro encapsulated dye. Paper designated CF or coated front has a layer of clay and resin that react with the dye from the CB paper to form an image when pressure is applied. CFB paper, or coated front and back, has both coatings applied allowing for transfer to itself and to the coated front beneath it. Click Here for an extended article and links concerning carbonless paper.
-
Case
The stiff covers of a hardbound book.
-
Case Binding
Books bound using hard board (case) covers. Typically known as a hardcover book.
-
Casein
A milk byproduct used as an adhesive in making coated papers.
-
Casing In
The process of placing in and adhering a book to its case covers.
-
Cast Coated
A paper that is coated and then pressure dried using a polished roller which imparts an enamel like hard gloss finish.
-
Catching Up
A term to describe that period of the printing process where the non-image areas can take on ink or debris.
-
Chain Lines
Lines that appear on laid paper as a result of the wires of the papermaking machine.
-
Chalking
A term used to describe the quality of print on paper where the absorption of the paper is so great that it breaks up the ink image creating loose pigment dust.
-
Chancery Italic
A 13th century handwriting style which is the roots of italic design.
-
Coarse Screen
Halftone screens commonly used in newsprint; up to 85 lines per inch.
-
Coated (Paper)
Paper coated with clay, white pigments and a binder. This yields characteristics that are better for printing because there is less picking and the ink stands out from the paper fiber instead of being absorbed by it. Various finishes can be achieved by this method varying from eggshell to glossy.
-
Coated Art Paper
Printing papers used for printing projects that require a special treatment of detail and shading.
-
Coated Stock
Any paper that has a mineral coating applied after the paper is made, giving the paper a smoother finish.
-
 Coil Binding, aka Spiral Binding
Coil Binding, aka Spiral BindingCoil binding is composed of a plastic or metal coil that looks similar to a spring. the coil is feed through specially punched holes and then is cut to size and crimped to keep the coil from backing out of the holes. Coil binding provides a book that will lie open and flat and is useful for applications such as cookbooks and manuals..
Three pieces of equipment are required for coil binding. A punch is used to create the holes along the edge of the document. Then a coil inserter is used to thread the coil through the holes in the cover. Some shops choose to do this step by hand. Finally the end of the coil is cut to size and then must be crimped to prevent the coil from coming loose from the book. Crimping and trimming of the coil can be done with either crimping pliers or machines that have been specially developed for that function.For more information on carbonless business form books and spiral binding CLICK HERE.
-
Cold Color
Any color that moves toward the blue side in the color spectrum.
-
Cold-Set Inks
A variety of inks that are in solid form originally but are melted in a hot press and then solidify when they contact paper.
-
Collate
To gather sheets or signatures together in their correct order. (see Gather) This is of course accomplished on a machine called a collator or done by hand in some small shops.
-
Collator
Machine used to assemble the various parts of a form into a finished product using glue or crimps. Typically, crash numbering is done on a collator.
-
Colophon
A printers or publishers identifying symbol or emblem.
-
 Color Bars
Color BarsThis term refers to a color test strip, which is printed on the waste portion of a press sheet. It is a standardized (GATF-Graphic Arts Technical Foundation) process which allows a pressman to determine the quality of the printed material relative to ink density, registration, and dot gain. It also includes the Star Target, which is a similar system designed to detect inking problems.
-
Color Separating
The processes of separating the primary color components for printing.
-
Color Strength
A term referring to the relative amount of pigmentation in an ink.
-
Color Transparency
Transparent film containing a positive photographic color image.
-
Column Gutter
Space between two or more columns of type on one page.
-
Commercial Register
Color registration measured within plus or minus one row of dots.
-
Composition
The process of preparing artwork for printing. It may include the assembly of characters into words, lines and paragraphs of text or body matter along with the placement of images for reproduction by printing. Also known as typesetting.
-
 Condensed Type
Condensed TypeA narrow, elongated type face.
-
Consecutive Numbering
Numbers printed in sequential order to allow the form to be controlled by the end user. e.g. 00001, 00002, 00003, etc. These numbers can either be printed by the press or crashed on the collator.
-
Continuous Forms
A form which is manufactured from a continuous web and is not cut into individual forms prior to use. Continuous forms are available in 1 part bond and carbonless or carbon interleaved formats. Multi-part forms must be collated prior to use.Fanfold continuous forms are perforated between forms for removal of the individual forms. Some continuous forms are also produced in non-folded roll formats. Typically continuous forms have stubs on both sides of the form with lineholes, to allow them to be fed into an impact printer.
-
Continuous Tone
Image made of non-discernable picture elements which give appearance of continuous spectrum of gray values or tones. Also known as a contone.
-
Contrast
The degree of tonal separation or gradation in the range from black to white.
-
Copy
Refers to any typewritten material, art, photos etc., to be used for the printing process.
-
Copy
All the text needed for a printing project.. It is usually marked up with instructions for the typesetter.
-
Corner Marks
Marks on a final printed sheet that indicate the trim lines or register indicators. See item "Crop" below.
-
Cover
A term describing a general type of papers used for the covers of books, pamphlets etc.
-
Cracking
Delamination.
-
 Crash Numbering
Crash NumberingConsecutive numbering on a form that uses carbon or the carbonless characteristics of the paper to transfer an image made by impact of the numbering machine on the first part to all the other parts of the form. Crash numbering is most often performed on the collator. The above image shows how the crashed number looks on the various parts of the form. (See Press Numbering Also)
-
Creep
1) When the rubber blanket on a cylinder moves forward due to contact with the plate or paper.
2) Movement of print in a booklet due to the added thickness of folded sheets being behind one another in a folded signature. The outer edges of sheets creep away from the back most fold as more folded sheets are inserted inside the booklet. Creep varies based on the number and thickness of the pages in a signature. When significant creep occurs, it must be compensated for in the design process or during imposition. -
Crop
To eliminate a portion of the art or copy as indicated by crop marks.
-
 Crop Mark
Crop MarkMarkings at edges of original or on guide sheet to indicate the area desired in reproduction with negative or plate trimmed (cropped) at the markings.
-
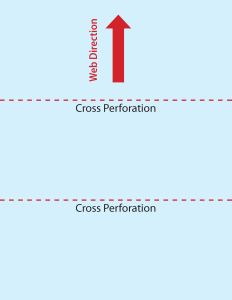 Cross Perforation
Cross PerforationA perforation that is cut at a right angle to the direction that the web is running through the press.
-
Cross-over
Elements that cross page boundaries and land on two consecutive pages (usually rules).
-
Crossmarks
Marks of fine lines, which intersect to indicate accurate alignment of art elements.
-
Crossover
A term used to describe the effect of ink from an image, rule or line art on one printed page, which carries over to another page of a bound work.
-
Curl
Not lying flat and tending to form into cylindrical or wavy shapes. A term to describe the differences of either side of a sheet relative to coatings, absorbency etc.; the concave side is the curl side.
-
Cut-off
A term used in web press printing to describe the point at which a sheet of paper is cut from the roll; usually this dimension is equal to the circumference of the cylinder. For example a 17 inch press has a cut-off of 17 inches. The number of forms up is divided by the cut-off size to give the number of cuts needed to finish a job. A job consisting of 1000 forms that was printed 4 up would need 250 cut-offs or cuts, to complete the job.
-
Cutter
Machine for accurately cutting stacks of paper to desired dimensions...can also be used to crease. Also trims out final bound books' top size (soft cover).
-
Cutting Die
Sharp edged device, usually made of steel, to cut paper, cardboard, etc., on a printing press.
-
 Cyan
CyanA shade of blue used in the four-color process; it reflects blue and green light and absorbs red.
-
Cylinder Gap
The gap in the cylinders of a press where the grippers or blanket clamps is housed.
-
Dahlgren
A dampening system for printing presses which utilizes more alcohol (25%) and less water; this greatly reduces the amount of paper that is spoiled.
-
Dampening
An essential part of the printing process whereby cloth covered rubber rollers distributes the dampening solution to the plate.
-
Dandy Roll
During the paper making process while the paper is still 90% water, it passes over a wire mesh cylinder (dandy roll), which imparts surface textures on the paper such as wove or laid. This is also the stage where the watermark is put onto the paper.
-
Deckle Edge
The rough or feathered edge of paper when left untrimmed. This edge is created during the paper making process where the pulp comes in contact with the deckle frame.
-
Delete
An instruction given to remove an element from a layout.
-
Demy
A term that describes a standard sized printing paper measuring 17.5 x 22.5 in.
-
Densitometer
An optical device used by printers and photographers to measure and control the density of color.
-
Density
The lay of paper fibers relative to tightness or looseness which affects the bulk, the absorbency and the finish of the paper.
-
Density
The degree of tone, weight of darkness or color within a photo or reproduction; measurable by the densitometer. Reference, densitometer.
-
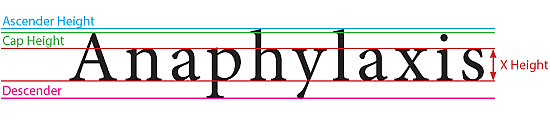 Descender
DescenderA term that describes that portion of lower case letters which extends below the main body of the letter, as in the letter "p" or y.
-
Desensitizing Ink
A specially formulated ink that stops the chemical process that causes the image transfer on coated front (CF) and coated front and back papers (CFB). In both cases desensitation occurs only on the coated front (CF) side of the paper
Desensitizing ink can be used to simulate the effect of a pattern or spot carbon while utilizing carbonless paper. The ink must be applied with care to insure that other areas of the paper are not desensitized by excess ink. As a general rule, no more than 60% of the area of the offset press blanket should be coated with desensitizing ink. To gain a fuller understanding of how carbonless paper works visit our Forms Knowledge Base by Clicking Here. -
 Designation
DesignationWords printed on a form, usually at the bottom, that provide instructions for the distribution of each section of the form. These words are also referred to as the "legend line". These words differ from marginal words in that they are usually printed in the base color of the document and are actually on the plate with the copy of the document.
-
Die
Design, letters or shapes, cut into metal (mostly brass) for stamping book covers or embossing. An engraved stamp used for impressing an image or design.
-
Die Cutting
A method of using sharp steel ruled stamps or rollers to cut various shapes i.e. labels, boxes, image shapes, either post press or in line. The process of cutting paper in a shape or design by the use of a wooden die or block in which are positioned steel rules in the shape of the desired pattern.
-
Die Stamping
An intaglio process for printing from images engraved into copper or steel plates.
-
Digital Proof
Color separation data is digitally stored and then exposed to color photographic paper creating a picture of the final product before it is actually printed.
-
Dimensional stability
The qualities of paper to stabilize its original size when undergoing pressure or exposed to moisture.
-
Display Type
Any type that stands out from the rest of the type on a page which attracts attention of the reader.
-
Distribution Rollers
In the printing process, the rubber coated rollers responsible for the distribution of ink from the fountain to the ink drum.
-
 Dog Ear
Dog EarWhen a corner of a page is turned down. Can be a problem with certain printing processes. May also occur when you fold into a fold (such as a letter fold). At the side of one of the creases you get an indentation. It may look like a small inverted triangle.
-
Dot
The smallest individual element of a halftone.
-
Dot Gain
Darkening of halftone image due to ink absorption in paper causing halftone dots to enlarge. This results in a printed image looking darker that it should. Dot gain can be compensated for in the design process.
-
Draw-down
A method used by ink makers to determine the color, quality and tone of ink. It entails the drawing of a spatula over a drop of ink, spreading it flat over the paper.
-
Drier
A term that describes any additives to ink which encourages the drying process.
-
Drill
The actual drilling of holes into paper for ring or comb binding.
-
Drop Folio
Page number printed at foot of page.
-
 Drop Shadow
Drop ShadowA shadow image placed strategically behind an image to create the affect of the image lifting off the page. The above image was created in Indesign CS 6.
-
Ductor Roller
The roller between the inking and the dampening rollers.
-
Dull Finish
Any matte finished paper.
-
Dummy
A term used to describe the preliminary assemblage of copy and art elements to be reproduced in the desired finished product; also called a comp.
-
Dummy Model
Resembling finished piece in every respect except that the pages and cover are blank, used by the designer as a final check on the appearance and +feel+ of the book as a guide for the size and position of elements on the jacket.
-
Duotone
Color reproduction from monochrome original. Keyplate usually printed in dark color for detail, second plate printed in light flat tints. A two-color halftone reproduction generated from a one-color photo.
-
Duplex Paper
Paper which has a different color or finish on each side.
-
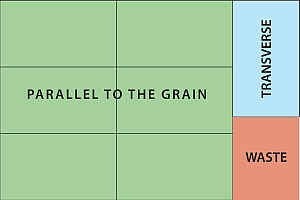 Dutch Cut
Dutch CutImposing items on a page in such a way that some of the items are cut from the paper parallel to the grain and others transverse or across the grain. This should only be done with items where paper grain is not important to the functionality of the finished piece. Dutch cutting is usually done to maximize yield from the sheet.
-
Dye-Based Ink
Any ink that acquires its color by the use of aniline pigments or dyes. Reference, aniline
-
Edge Glue
To join a business form together with a thin glue line along the edge of the form. The most common position is "edge glue top". But typically any edge can be glued depending on the type of form. The form is separated by pulling the various plys apart. This type of form does not have a stub.
To gain a clear understanding of the different types of business forms Click Here. -
Eggshell Finish
The finish of paper surface that resembles an eggshell achieved by omitting the calendar process. Reference, calendar rolls.
-
Electronic Composition
The assembly of characters into words, lines and paragraphs of text or body matter with graphic elements in page layout form in digital format for reproduction by printing.
-
Electronic Proof
A process of generating a prepress proof in which paper is electronically exposed to the color separation negatives; the paper is passed through the electrically charged pigmented toners, which adhere electrostatically, resulting in the finished proof.
-
Elliptical Dot
Halftone screens in which the dots are actually elongated to produce improved middle tones.
-
Em
A unit of measurement equaling 12 points or 4.5mm.
-
Embossed
A method of paper finishing whereby a pattern is pressed into the paper when it is dry.
-
Embossing
To raise in relief a design or letters already printed on card stock or heavy paper by an uninked block or die. In rubber and plastic plate making the process is usually done by heat.
-
Enamel
A term that describes a glossy coating on paper.
-
Endsheet
Attaching the final sheet of a signature of a book to the binding.
-
English Finish
A grade of uncoated book paper with a smooth uniform surface.
-
Engraving
A printing process whereby images such as copy or art are etched onto a plate. When ink is applied, these etched areas act as small wells to hold the ink; paper is forced against this die and the ink is lifted out of the etched areas creating raised images on the paper.
-
Estimate
The form used by the printer to calculate the project for the print buyer. This form contains the basic parameters of the project including size, quantity, colors, bleeds, photos etc.
-
Estimator
One who computes or approximates the cost of work to be done on which quotation may be based.
-
Even Smalls
The use of smaller sized capitals at the beginning of a sentence without the use of larger sized caps.
-
 Extended or Expanded Type
Extended or Expanded TypeType with width greater than normal producing a rectangular effect.
-
Extender
A white pigment added to a colored pigment to reduce its intensity and improve its working qualities.
-
Extraneous Ink
Ink which was not designed to be on the printed piece. This may include drips, splatter, scratches and any other method that causes extra ink to be applied to an area unintentionally.
Magnetic Ink: Any ink which does not consist of the printed E13B characters, which is located in the MICR clear band. This ink may cause the document to be either unreadable or to read incorrectly.
-
F&G
A term in the binding process referring to folding and gathering.
-
Fan Apart Padding
The binding of carbonless forms together utilizing specially formulated glue which is actived only by the coated face (CF) or coated back (CB) of a document. Because the padding compound does not adhere to the uncoated surfaces of the document, the forms may be "fanned apart" into individual form sets when the glue is dry. The forms are usually produced using pre-collated carbonless sets. This type of padding is used in the production of either digital or sheet fed press produced carbonless forms. Only certain grades of carbonless paper are fan apart paddable. This process is analogous to edge gluing using a collator.
-
Fan Fold
Paper folding that emulates an accordion or fan, the folds being alternating and parallel.
-
Fat Face
Type that is quite varied in its use of very thin and very wide strokes.
-
Felt
A cloth conveyor belt that receives papers from the Fourdrinier wire and delivers it to the drier.
-
Felt Finish
The smoother side of paper, usually a soft weave pattern used for book papers.
-
Felt Side
It is the top side of the sheet in the paper making process that does not lie on the Fourdrinier wire.
-
Filling In
A fault in printing where the ink fills in the fine line or halftone dot areas.
-
Film Coat
Also called wash coat; any thinly coated paper stock.
-
Finish
The surface quality of paper.
-
Finish (Paper)
Dull - (low gloss) also matte or matte gloss.
-
Fist
A symbol used in printing to indicate the index; seen as a pointing finger on a hand "+".
-
Fit
The registration of items within a given page.
-
Flash Point
A term given to the lowest temperature of ignitibility of vapors given off by a substance.
-
Flat Charge
A charge added to a print job that remains constant. This charge is not affected by the quantity ordered. Flat charges are usually a one time charge for extra work that must be performed outside of the usual workflow.
-
Flood Coat
Printing over the entire face of a page with color. Depending on the type of ink and results desired the flood coat may or may not be screened. This process is most often used to change the color of white paper to another color.
-
Flush Cover
A bound book or booklet etc. having the cover trimmed to the same size as the text.
-
Flush Left
Typesetting that is aligned to the left hand side of the document margin. This results in what is known as "rag right "on the right hand side of the column of text.
-
Flush Right
Typesetting that is aligned to the right hand side of the document margin. This results in what is known as "rag left "on the left hand side of the column of text.
-
Fogging Back
Lowering density of an image in a specific area usually to make type more legible while still letting image show through.
-
Fold Marks
Markings at top edges that show where folds should occur.
-
Folder
Machine used to fold signatures down into sections.
-
Folio or Page Number
Number of page at top or bottom either centered, flushed left or flushed right often with running headline.
-
Font
The characters which make up a complete typeface and size.
-
Form Rollers
The rollers that come into direct contact with the plate of a printing press.
-
Forwarding
In Binding, the process between folding sheets and casing in, such as rounding and backing, putting on headbands, reinforcing backs, etc.
-
Fountain Solution
Offset lithography is based on the use of plates that have both oleophilic (oil loving) and hydrophilic (water loving) areas. The fountain solution is applied by the dampening system of the press to the plate allowing the hydrophilic area of the plate to repel ink. Fountain solution is a water based mixture that contains acid or bases depending on the desired pH, an organic or synthetic gum, a wetting agent such as alcohol or a alcohol substitute to reduce the surface tension of the water to make it flow more readily, fungicide to kill bacteria in the solution and some form of anti-foaming agent. A proper ink water balance is essential to quality printing.
-
Fourdrinier
A machine with a copper wire screen that receives the pulp slurry in the paper making process which will become the final paper sheet.
-
Free sheet
Paper that does not contain wood pulp impurities such as lignin but is composed primarily of cellulose fibers. Lignin is a complex polymer that partially comprises the secondary cell wall of plants. Lignin deteriorates over time and is undesirable in the production of quality paper.
-
French Fold(er)
Folder with printing on one side so that when folded once in each direction, the printing on outside of the folds.
-
Fringe
A halo that appears around halftone dots.
-
Fuzz
A term for the fibers that project from the paper surface.
-
GIF
A GIF is a compressed file format most often used on the web. This format is best utilised when you are working with images with clear sharp edges, smooth color gradations and text. A GIF allows you to use transparency and to create animationed images. Typically GIF's are not used in art for the printing process. GIF stands for Graphical Interchange Format
-
GIGO
Garbage in, garbage out.
-
Gang
The imposition of multiple images of a job or jobs on a plate to get the optimum yield from the sheet of paper being printed on.
-
 Gap
GapUnprintable area created by the need to have an area to lock the plate onto the plate cylinder. Typically the gap on a press is around a 1/2". Gap may vary by manufacturer or even by a small amount on presses from the same manufacturer. The gap runs the entire length of a snap apart set. Gap is also referred to as lockup. When designing print items for web presses it is good to know what size gap needs to be allowed for in the design. This information should be available from your forms manufacturer.
-
Gather
To assemble or collect sections into single copies of complete books for binding.
-
Gathering
Assembling sheets of paper and signatures into their proper sequence; collating.
-
Ghosting
Marring a print by the placement of an image of work printed on the reverse side which has interfered with its drying so that differences in the trapping frame colors or glass variations are apparent.
-
Ghosting
Image which appears as a lighter area on a subsequent print due to local blanket depressions from previous image areas on a letterpress rotary machine as well as on an offset press.
-
Glassine
A strong, smooth, translucent, super calendared paper that has a neutral pH. It is considered to be food safe and provides protection from grease, air, moisture and water. It has been utilized for envelope windows, food packaging, philately envelopes, and hinges, firecracker packaging, and envelopes for the storage of various items such as entomologist field specimens. For more information, Click Here to be redirected to JBM Glassine a manufacturer of glassine envelopes.
-
Gloss Ink
Quick drying oil based inks with low penetration qualities, used on coated stock.
-
Glyphic
A carved as opposed to scripted typeface.
-
Goldenrod
An orange colored paper with gridlines, used to assemble materials for exposure for platemaking.
-
Graduated Screen
An area of image where halftone dots range continuously from one density to another.
-
Grain
Direction of fibers in a sheet of paper governing paper properties such as increased size changes with relative humidity, across the grain, and better folding properties along the grain. For more information (Click Here.)
-
Grained Paper
A paper embossed to resemble various textures, such as leather, alligator, wood, etc.
-
Gravure
A printing process that uses a plate that is etched allowing the ink to flow into the groves before being transferred to the paper. This type of printing is also referred to as intaglio printing.
-
Gripper
A series of metal fingers that hold each sheet of paper as it passes through the various stages of the printing process.
-
Gripper Edge
The grippers of the printing press move the paper through the press by holding onto the leading edge of the sheet; this edge is the gripper edge. When designing items for print this is considered a non-printable area. Gripper area varies from press to press.
-
Groundwood
Low cost papers such as newsprint made by the mechanical pulping process as opposed to chemical pulping and refining.
-
Gumming
The application of gum arabic to the non printing areas of a plate.
-
Gutter
Space between pages in the printing frame of a book, or inside margin towards the back or binding edge. The blank space or margin between the type page and the binding of a book.
-
Hairline register
Printing registration that lies within the range of plus or minus one half row of dots. It is the thinnest of the standard printers' rules.
-
Halftone
Tone graduated image composed of varying sized dots or lines, with equidistant centers.
-
Hard Dot
The effect in a photograph where a dot has such a small degree of halation that the dot shows quite sharp.
-
Head Margin
That space which lies between the top of the printed copy and the trimmed edge.
-
Head to Foot
Copy on which the top of the back copy is at the foot of the face copy. Also called tumble style.
-
Head to Head
Copy on which the copy on the face and back are both at the top of the form.
-
Hickies
Repeating imperfections in printing caused by dirt, dried ink or other contamination on the plate or blanket. Usually a hickey has a dark center with a white halo around the contamination causing the hickey.
-
High Bulk Paper
Paper stock that is comparatively thick in relation to its basis weight.
-
High Key Halftone
A halftone that is made utilizing only the highlight tones down through the middle tones.
-
Highlight Dot
The highest density of a halftone image.
-
Highlights
The lightest tones of a photo, printed halftone or illustration. In the finished halftone, these highlights are represented by the finest dots.
-
Hollow
That space on the spine of a case bound book between the block of the book and the case binding.
-
Hot melt
An adhesive used in the binding process, which requires heat for application.
-
House Sheet
This is a term that refers to a paper that a printer keeps on hand in his shop.
-
IBC
Inside back cover.
-
IFC
Inside front cover.
-
Image Area
That portion of the printing plate that carries the ink and prints on paper.
-
Image Setter
High resolution, large format device for producing film from electronically generated page layouts.
-
Imposition
Arrangement of pages so that they print correctly on a press sheet, and the pages are in proper order when the sheets are folded.
-
Impression
Product resulting from one cycle of printing machine. The pressure of the image carrier, whether it be the type, plate or blanket, when it contacts the paper.
-
Index Bristol
A relatively thick paper stock; basis size---25 1/2 x 30 1/2.
-
Indicia
Markings pre-printed on mailing envelopes to replace the stamp.
-
Ink Fountain
The device which stores and meters ink to the inking rollers.
-
Ink Holdout
A quality of paper to be resistant to ink absorption, allowing the ink to dry on the paper surface.
-
Ink Setting
The inertial resistance to flow that occurs to ink as soon as it is printed.
-
Inserts
Extra printed pages inserted loosely into printed pieces.
-
Interleaves
Extra blank pages inserted loosely into book after printing.
-
Italic
Text that is used to denote emphasis by slanting the type body forward.
-
JPEG
Is a lossy file compession standard utilised to make large images smaller and easier to store and transmit digitally. JPEG's are smaller than files compressed with lossless compression. JPEG compression is best used to compress photographs and artwork. In printing, a high quality JPEG can be used for process printing for items such as brochures and calendar photos. JPEG"s cannot typically be used in jobs that require spot colors. JPEG's that came from a website are usually too low in quality to use for art in projects. JPEG stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group. A general rule of thumb for all graphics used in printing is that they need to be at least 300 dpi.
-
Jacket
The paper cover sometimes called the "dust cover" of a hardbound book.
-
Job Number
A number assigned to a printing project used for record keeping and job tracking. Also used to retrieve old jobs for reprints or reworking by customer.
-
Jog
To vibrate a stack of finished pages so that they are tightly aligned for final trimming.
-
Jogger
Vibrating, sloping platform that evens up the edges of stacks of paper.
-
Kerning
The narrowing of space between two letters so that they become closer and take up less space on the page.
-
Kerning
Refers to the adjustment of space individual characters in a headline to give the appearance that they appear to be evenly spaced. Usually kerning is accomplished by by diminishing the space between certain characters.
-
Key Plate
The printing plate that is used as a guide for the other plates in the color printing process; it usually has the most detail.
-
Keying
The use of symbols, usually letters, to code copy that will appear on a dummy.
-
Keyline
Lines that are drawn on artwork that indicate the exact placement, shape and size of elements including halftones, illustrations etc.
-
Kraft
A coarse unbleached paper used for printing and industrial products.
-
Lacquer
A clear gloss coating applied to printed material for strength, appearance and protection.
-
Laid Paper
Paper that is processed with parallel lines to give the appearance of having been handmade. The lines simulate the screens that are used in the process of hand making paper. Smooth finish paper is called wove finish paper.
-
Laser Engraving
A paper cutting technique whereby laser technology is utilized to cut away certain unmasked areas of the paper. The cutting is a result of the exposure of the paper to the laser ray, which actually evaporates the paper.
-
Lay Edge
Edge of a sheet of paper being fed into a printing press.
-
Layout
A rendition that shows the placement of all the elements, roughs, thumbnails etc., of the final printed piece before it goes to print.
-
Leaders
The dots or dashes used in type to guide the eye from one set of type to the next.
-
 Leading
LeadingSpace between lines of type; the distance in points between one baseline and the next. So called because in the days of letter press printing, thin lead spacers of varying point sizes were used to provide space between the lines of cast type.
-
Leaf
One of a number of folds (each containing two pages) which comprises a book or manuscript.
-
Ledger Paper
A stiff heavy business paper generally used for keeping records.
-
Letterpress
Printing that utilizes inked raised surfaces to create the image.
-
Letterspacing
The addition of space between typeset letters to achieve the purpose of filling a specific area.
-
Line Copy
Any copy that can be reproduced without the use of halftone screens.
-
Linen
A paper that emulates the look and texture of linen cloth.
-
Lithocoated Paper
A paper that is coated with a special water-resistant material which is able to withstand the lithographic process.
-
Lithography
The process of printing that utilizes flat inked surfaces to create the printed images.
-
Lock Up
Unprintable area created by the need to have an area to lock the plate onto the plate cylinder. Typically the lock up on a press is around a 1/2". Lock up may vary by manufacturer or even by a small amount on presses from the same manufacturer. The lock up runs the entire length of a snap apart set. Lockup is also referred to as gap. When designing print items for web presses it is good to know what size lock up needs to be allowed for in the design. This information should be available from your forms manufacturer. See the photo at entry for "Gap".
-
Logotype
A personalized type or design symbol for a company or product. It uses consistent type to project an image of the company in all written forms of communication.
-
M weight
The actual weight of 1000 sheets of any given size of paper.
-
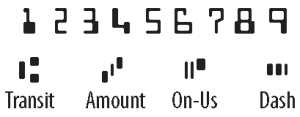 MICR
MICRAcronym for "Magnetic Ink Character Recognition. MICR ink usually contains magnetized particles of iron oxide and is printed with a special character set (E13B) that renders them machine readable. This allows for the machine fast and reliable processing of checks and other documents to return them to the issuing institution. It contains the numbers 1-9 and the following symbols, transit, amount, On-Us, and dash.
-
MICR Clear Band
A 5/8" band parallel to the bottom edge of a MICR document in which no extraneous MICR ink can occur.
-
Machine Coated
Paper that has had a coating applied to either one or two of its sides during the papermaking process.
-
Machine Direction
An alternate term for grain direction.
-
Machine Finish
A paper finish that results from the interaction of the paper with the Fourdrinier process as opposed to post machine embossing. Reference, Fourdrinier
-
Magnetic Black
Black pigments containing black iron oxides, used for magnetic ink character recognition.
-
Make Rready
Process of adjusting final plate on the press to fine tune or modify plate surface.
-
Manifold / Manifolding
To make copies of. Specifically, as referring to the copies made using carbon or carbonless paper when writing upon it. This is why business forms are sometimes referred to as manifold business forms.
-
Margin
Refers to the space left from the edge of the text to the edge of the page. Typically margin is allowed on all four sides of a printed text piece.
-
 Marginal Words
Marginal WordsWords usually printed in red ink at the top or bottom of a form that allow each portion of the form to be routed to the correct recipient.
-
Mark-up
To write up instructions, as on a dummy.
-
Matte Finish
A coated paper finish that goes through minimal calendaring. The surface of the paper appears uniformly smooth and is without luster or glare. Reference, calendaring.
-
Mechanical
A term used to describe finished artwork that is camera ready for reproduction, including all type, photos, illustrations etc.
-
Metropolitan Service Area
A group of ZIP codes usually in close proximity defining a large metropolitan area (e.g. New York City or Los Angeles).
-
Midtone Dot
Commonly taken as the area between highlight and shadow area of a subject's face in halftone image.
-
Moire
An undesirable halftone pattern produced by the incorrect angles of overprinting halftone screens.
-
Molleton
A cotton fabric used on the dampening rollers of a printing press.
-
Mottle
A term used to describe spotty or uneven ink absorption.
-
Mullen Testing
A specific test of tensile paper strength; an important factor if web presses are used for printing.
-
NCR Paper
No Carbon Required. Paper that was developed as an alternative to using carbon sheets between parts of business forms to transfer the image from part to part. See also CB, CF, and CFB definitions..
-
Natural
A term to describe papers that have a color similar to that of wood; also called cream, off-white or ivory.
-
Negative
Film that contains the same images as the original print, except that all colors and shades are reversed. Reference, positive.
-
Newsprint
A light, low cost groundwood paper made especially for newspapers. Reference, groundwood.
-
Nominal Weight
When the basis weight of paper differs from the actual weight, the term nominal weight is used.
-
OA Of Register
When two sheet passes on a press are misaligned.
-
OBC
Outside back cover.
-
OFC
Outside front cover.
-
Oblong
A term used to describe printed books, catalogs etc., that are bound on their shorter side; also referred to as album bound.
-
Off-shore Paper
Any papers made outside the US and Canada.
-
Offset
The most commonly used printing method, whereby the printed material does not receive the ink directly from the printing plate but from an intermediary cylinder called a blanket which receives the ink from the plate and transfers it to the paper.
-
Offset Lithography
Indirect printing method, introduced in 1905, in which the inked image on the press-plate is first printed onto a rubber blanket, then in turn offsets the inked impression on to the sheet of paper. This type of printing is based on the concept that oil and water do not mix. Thin aluminum plates are used which have a hydrophilic (water attracting) surface and an oliophilic (oil attracting) area that the ink adheres to. Rollers reapply water and ink on each rotation of the press cylinder allowing for a continuous web to be printed by the press or many sheets on after another. Offset lithography is the predominant form of printing used today.
-
Offset Paper
A term for uncoated book paper.
-
Offsetting
Problem that occurs when ink application is too high and the wet image transfers to the back of the next page or the back of the web when it is rolled up. Offsetting is avoided by judicious setting of water and ink balance making sure that only enough ink is laid down to provide dense coverage but still has time to absorb into the paper and to dry.
-
Opacity
Quality of papers that defines its opaqueness or ability to prevent two-sided printing from showing through.
-
Opaque
A quality of paper that allows relatively little light to pass through.
-
Opaque Ink
Ink that completely covers any ink under itself.
-
Over Run
Surplus of copies printed.
-
Overhang Cover
A cover of a book that extends over the trimmed signatures it contains.
-
Overprinting
Any printing that is done on an area that has already been printed.
-
Overset
Type that is set in excess of the allotted space.
-
PMS
Pantone Matching System
-
PNG
A file format developed as a general replacement, on the web, for the GIF format due in part to legal issues relating to the LZW compression alogrithim and the limitations of the GIF format. The PNG file is superior the the GIF in a number of ways. First, it allows for loseless compression while maintaining a small file size. Secondly, it supports indexed color both in grayscale and RGB. Third, with its alpha channel, it is able to have various levels of opacity, allowing for varying degrees of transparency. The PNG does not support multiple images in the same file so animation is not supported. PNG stands for Portable Network Graphic. PNG's can be utilized in the printing process for some applications. A general rule of thumb for all graphics used in printing is that they need to be at least 300 dpi.
-
 Padding
PaddingThe application of a special glue to bind forms together into sets. This glue, when dry, allows a single set or single form to be removed while the other forms remain bound together.
-
Page
One side of a leaf.
-
Page Makeup
The assemblage of all the necessary elements required to complete a page.
-
Page Proofs
Proofs made up from pages.
-
Pagination
The orderly arrangement of pages in a book so that they are in the correct order when printed and bound. This is usually accomplished through the process of imposition.
-
Pantograph
Background printing on a document that contains a pattern or flat screen. The pantograph is usually printed in a light or screened ink, and is either decorative in nature or provides an antialteration feature for the document. Pantographs can be branded using a company or organizational logo as the repeating background pattern.
-
Paperboard
Any paper with a thickness (caliper) of 12 points (.3mm) or more.
-
Parchment
A hard finished paper that emulates animal skin; used for documents, such as awards, that require writing by hand.
-
Parent Sheet
A sheet that is larger than the cut stock of the same paper.
-
Paste-up
Preparation of positive materials into a layout for photographing to film negatives.
-
Pattern Or Spot Carbon
Custom made carbon paper which has carbon only in a specified area. This allows for the transfer of an image on a business form in only the specific area that has carbon applied to the paper. Unless a print shop is able to make their own spot carbon, this causes longer lead times to the form production process. The carbon must be ordered, manufactured by a carbon paper manufacturer and then shipped to the plant to be interleaved with the business form.
In some applications, desensitizing ink applied to carbonless business forms paper (NCR) can provide some of the same functionality. Typically desensitizing ink can be applied to an area of not greater than 60% of the area of the blanket being used to print the form. -
Peeling
Delamination.
-
Per M
Forms are usually quoted by the "M". This is Roman numeral for 1000.
-
Perf Marks
Markings usually dotted lines at edges showing where perforations should occur.
-
Perfect
A term used to describe the binding process where the signatures of a book are held together by a flexible adhesive.
-
Perfect Binding
Binding process where backs of sections are cut off, roughened and glued together, and rung in a cover.
-
Perfecting
Printing both sides of the paper (or other material) on the same pass through the printing machine.
-
Perfecting Press
A printing press that prints on both sides of the page in a single pass.
-
Perforating
Punching small holes or slits in a sheet of paper or cardboard to facilitate tearing along a desired line.
-
Pica
Standard of measurement, 1/6 inch. 1 pica = 12 points, 72 points = 1 inch
-
Picking (1)
When the tack of ink is stronger than the surface strength of the paper, some lifting of the paper surface occurs; this is referred to as picking.
-
Picking (2)
An occurrence in printing whereby the tack of ink pulls fibers or coating off the paper surface, leaving spots on the printed surface.
-
Piling
A build up of pigment or paper coatings onto the plate, blankets or rollers.
-
Pinholing
Failure of printed ink to form a completely continuous film, visible in the form of small holes in the printed areas.
-
Plastic Comb
A method of binding books whereby holes are drilled on the side closest the spine, and a plastic grasping device is inserted to hold the pages together.
-
Plate
Reproduction of type or cuts in metal, plastic, rubber, or other material, to form a plate bearing a relief, planographic or intaglio printing surface.
-
Plate Cylinder
The cylinder on a printing press on which the plate is mounted.
-
Plate Finish
Any bond, cover or bristol stock with an extremely smooth finish achieved by calendaring.
-
Platemaking
Making a printing plate from a film or flat including preparation of the plate surface, sensitizing, exposing through the flat, developing or processing, and finishing.
-
Point
A measurement unit equal to 1/72 of an inch. 12 points to a pica, 72 points to an inch.
-
 Point Size
Point SizeTypesetting term referring to the measurement of a typeface from the ascender line to the descender line. Even though type may be the same point size it may still vary greatly in size when compared to another typeface of the same point size. See example above.
-
Positive
Film that contains an image with the same tonal values as the original; opposite of a negative.
-
Ppi
Pixels per inch.
-
Premium
Any paper that is considered better than #1 by its manufacturer.
-
 Press Numbering
Press NumberingNumbering where the form is numbered as it is produced on the press. The number is usually printed in the same color on all parts. Crash numbering is usually red or black on the first part, and the color of the carbon or carbonless transfer color of blue or black on the other parts. (See Crash Numbering)
-
Press-Proof
Actual press sheet to show image, tone values and colors as well as imposition of frame or press-plate.
-
Primary Colors
In printing the four primary colors are cyan (blue), magenta (red), yellow and black.
-
Printability
The quality of papers to show reproduced printed images.
-
Printers Pairs
Two consecutive pages as they appear on a flat or signature.
-
Process Inks
Printing inks, usually in sets of four colors. The most frequent combination is yellow, magenta, cyan, and black, which are printed, one over another in that order, to obtain a colored print with the desired hues, whites, blacks, and grays.
-
Process Printing
Printing from two or more half tones to produce intermediate colors and shades.
-
Progressive Proofs
Any proofs made from the separate plates of a multi-plate-printing project.
-
Proof
Impression from composed type or blocks, taken for checking and correction, from a lithographic plate to check accuracy of layout, type matter, tone and color reproduction.
-
Pull Quote
A quote pulled from the text and emphasized by displaying it in a larger or different type than the main body of the text.
-
Rag paper
Papers with a complete or partial content of cotton fibers.
-
Ragged Left
The term given to right-justified type that is uneven on the left.
-
Ragged Right
The term given to left-justified type that is uneven on the right.
-
Railroad Board
A thick, coated paper used for signs; usually waterproof.
-
Readers Pairs
Two consecutive pages as they appear in printed piece.
-
Readibility
The goal of typesetting is to produce copy that is easy to be read on the finished page. Type size, columns, leading, the color of the type and the color of the page all play a part in a design that has ease of readability.
-
Ream
500 sheets of paper.
-
Recto
The odd numbered pages (right hand side) of books.
-
Reel
The master roll of paper as it comes off the papermaking machine. It is in its original width and is then cut into smaller rolls.
-
Register
The arrangement of two or more images in exact alignment with each other.
-
Register Marks
Any crossmarks or other symbols used on layout to assure proper registration.
-
Reversed Type
Type that is set in white with against a darker background. The best practice is to set the type in a bold sans serif font . Fonts with fine serifs such as Time, Times Roman, Minion, etc., should be avoided as their serif areas easily fill with ink and lead to an obscuring or closing up of the text.
-
Right Angle Fold
A term that denotes folds that are 90 degrees to each other.
-
Roll To Roll
A web press printing process where the roll of paper is printed and stored on a roll to be shipped or sent to a collator for further processing. The collator can be used to bind the various parts into forms, if using carbonless paper or add carbon or crash numbering to the the forms.
-
Rubine
A pigment somewhat redder than true magenta.
-
Run-Around
A term given to copy that accommodates the lines of a picture or other image or copy.
-
Runability
A term used to describe how well a paper runs on a printing press.
-
Running Head
A title at the top of a page that appears on all pages of a book or chapter of a book.
-
Saddle Stitching
Stitching where the wire staples pass through the spine from the outside and are clinched in the center. Only used with folded sections, either single sections or two or more sections inset to form a single section.
-
Safety Paper
A paper that shows sign of erasure so that it cannot be altered or tampered with easily.
-
Satin Finish
A smooth delicately embossed finished paper with sheen.
-
Scaling
The enlargement or reduction of an image or copy to fit a specific area.
-
Score
Impressions or cuts in flat material to facilitate bending or tearing.
-
Screen Angles
The placement of halftone screens to avoid unwanted moire patterns. Frequently used angles are black 45deg, magenta 75deg, yellow 90deg, and cyan 105deg.
-
Screen Ruling
A measurement equaling the number of lines or dots per inch on a halftone screen.
-
Screened Print
A photo print made by using a halftone negative; also called a velox.
-
Scumming
Scumming happens because the plate begins to take up ink on the non image area of the plate. It is most often caused by poor water ink balance.
-
Self Cover
A booklet which has a cover made out of the same type of paper stock as the internal pages.
-
Shadow Dot
The lowest density of a halftone image.
-
Sharpen
To decrease the dot size of the halftone which in turn decreases the color strength.
-
Sheetwise
The printing of two different images on two different sides of a sheet of paper by turning the page over after the first side is printed and using the same gripper and side guides.
-
Shootable Copy
Copy that can be scanned or shot with a camera that reproduces a high quality copy of the original. Copy needs to smooth, clean and printed in a dark ink.. Forms with areas that are screened, have pantographs, areas of uneven ink or bleed through of the backer are not considered suitable candidates for shootable copy. Also called camera ready copy.
-
Show Through
A problem that occurs when the printing on one side of a sheet is seen from the other side.
-
Side Guide
The guides on the sides of the sheet fed press that position the sheet sideways as the paper is led towards the front guides.
-
Side Stitching
Stitching where the wire staples pass through the pile of sections or leaves gathered upon each other and are clinched on the underside.
-
Signature (Section)
Printed sheet (or its flat) that consists of a number of pages of a book, placed so that they will fold and bind together as a section of a book. The printed sheet after folding.
-
Silhouette halftone
A halftone with the background screen removed.
-
Slitting
A term to describe the process of cutting of printed sheets by the cutting wheels of a printing press.
-
Smoothness
That quality of paper defined by its levelness which allows for pressure consistency in printing, assuring uniformity of print.
-
Soft Dot
An excessively large halo around a dot in a photograph that causes a fringe that diminishes the dot intensity.
-
Spine
Back edge of a book.
-
Spiral Binding, aka coil binding
Coil binding is composed of a plastic or metal coil that looks similar to a spring. the coil is feed through specially punched holes and then is cut to size and crimped to keep the coil from backing out of the holes. Coil binding provides a book that will lie open and flat and is useful for many applications.
Three pieces of equipment are required for coil binding. A punch is used to create the holes along the edge of the document. Then a coil inserter is used to thread the coil through the holes in the cover. Some shops choose to do this step by hand. Finally the end of the coil is cut to size and then must be crimped to prevent the coil from coming loose from the book. Crimping and trimming of the coil can be done with either crimping pliers or machines that have been specially developed for that function.For more information on business form books and spiral binding CLICK HERE.
-
Spot Carbon Or Pattern Carbon
Custom made carbon paper which has carbon only in a specified area. This allows for the transfer of an image on a business form in only the specific area that has carbon applied to the paper. Unless a print shop is able to make their own spot carbon, this causes longer lead times to the form production process. The carbon must be ordered, manufactured by a carbon paper manufacturer and then shipped to the plant to be interleaved with the business form.
In some applications, desensitizing ink applied to carbonless business forms paper (NCR) can provide some of the same functionality. Typically desensitizing ink can be applied to an area of not greater than 60% of the area of the blanket being used to print the form. -
Spot Color
Small area printed in a second color.
-
Spot Varnish
Varnish applied to an area to highlight it from the rest of the printed piece. For example spot varnish could be applied to water drops on a printed piece to make them look wet. The effect can be applied to any area that you would like to “pop out” on the printed piece.
-
Spread
A film image that is larger than the original image to accommodate ink trapping. Reference, trapping
-
Stability
The quality of paper to maintain its original size when it undergoes pressure and moisture changes.
-
Stagger Cutting
A process of cutting many sheets from the same parent sheet in which the smaller sheets have different grain directions; also called dutch or bastard cutting.
-
Static Neutralizer
A device on a printing press that minimizes the amount of static build up on paper as it passes through the press.
-
Step And Repeat
A process of generating multiple exposures by taking an image and stepping it according to a predetermined layout.
-
Stet
A proofreader's symbol that is usually written in the copy margin, that indicates that the copy, which was marked for correction, should be left as it was.
-
Stock
A term for unprinted paper or other material to be printed.
-
Strip-In
To add an element, such as copy that is shot separately, and then stripped into place on a goldenrod flat.
-
Stripping
Originally, the removal of the photographic emulsion with its image from individual negatives and combining them in position on a glass plate. Now the use of stripfilm materials, and the cutting, attachment, and other operations for assembling. The positioning of positives and negatives on the flat before proceeding to platemaking.
-
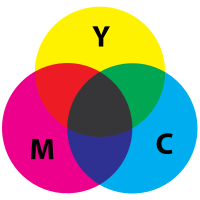 Subtractive Color
Subtractive ColorColor model based on the subtracting (absorption) of certain wavelengths of light and the reflection of others to produce various colors. Colors seen are based on what colors of the spectrum are reflected by the surface of an object and is made visible. The basic components of this color model are Cyan, Magenta, and Yellow. In printing this is the CMY of process color printing. True black cannot be made in this model so K or Black is added to complete the spectrum. The gamut of color reproduction is limited to around 20% of visible colors.
-
Super Calendaring
A machine procedure that produces a high finished paper surface that is extremely smooth and exceptional for printing.
-
Synthetic Papers
Any petroleum based waterproof papers with a high tensile strength.
-
Tabloid
Paper that is 11" x 17".
-
Tack
The adhesive quality of inks.
-
Tag
A dense, strong paper stock.
-
Tensile Strength
A paper's ability to withstand pressure.
-
Text
A high quality printing paper.
-
Thermography
A printing process whereby slow drying ink is applied to paper and while the ink is still wet, it is lightly dusted with a resinous powder. The paper then passes through a heat chamber where the powder melts and fuses with the ink to produce a raised surface.
-
Tint
A halftone screen that contains all the same sized dots.
-
Tooth
The rough surfaced finish of papers such as vellum or antique.
-
Transparent
Inks that do not block out the colored inks that they print over, but instead blend with them to create intermediate colors.
-
Trapping
The process of printing wet ink over printed ink which may be wet or dry.
-
Trim Marks
Marks placed on the sheet to indicate where to cut the page.
-
Tumble Style
Copy on which the top of the back copy is at the foot of the face copy. Also called head to foot.
-
 Turn Bar
Turn BarOn web presses, the paper must be turned to allow for printing on the front and back. This is accomplished by the use of the turn bar. After the back has been printed paper is rotated on the press by running it through the turn bar. It is usually located just after the the last back print station.
-
Twin Wire Machine
Fourdrinier papermaking machines with two wires, instead of a wire and felt side. This assures higher quality when two sides are used for printing.
-
Two-sidedness
The difference in feel and appearance of either side of a sheet of paper due to the papermaking process having a felt and wire side.
-
Type Family
All the variations of a font including bold, italic, normal, light, condensed, etc.
-
Typo
Abbreviated form of the words "typographical error". This refers to errors made in the typesetting or processing of a printed document. The goal of proofing is to detect and correct such errors..
-
Uncalendared
Papers that are not smoothed by going through the calendaring process.
-
Up
A term used to describe how many similar sheets can be produced on a larger sheet; two up, four up, etc.
-
Upright
A term given to books bound on the longer dimension.
-
Varnish
A clear shiny ink used to add gloss to printed pieces. The primary component of the ink vehicle. Reference, vehicle.
-
Vehicle
A combination of varnish, waxes, dryers etc., that contain the pigment of inks and control the flow, the drying and the adhesion of the pigments to the printed surface.
-
Vellum
A finish of paper that is rough, bulky and has a degree of tooth.
-
Verso
A term given to the left-hand or even-numbered pages of a book.
-
Vignette
Fade to white or small decorative design or illustration. A photo or illustration etc., in which the tones fade gradually away until they blend with the surface they are printed on.
-
W&B
An abbreviation for work and back. Reference, sheetwise.
-
W&T
An abbreviation for work and turn.
-
Walk-off
A term given to the occurrence of plate deterioration of the image area during the printing process; usually occurs on long runs.
-
Washup
The procedure of cleaning a particular ink from all of the printing elements (rollers, plate, ink fountain etc.) of a press. On presses using Pantone or spot colors the addition of a color necessitates a washup charge being added to a quote.
-
Watermark
A translucent logo that is embossed during the papermaking process while the paper slurry is on the dandy roll. Reference, dandy roll
-
Web
The roll of paper that is used in web or rotary printing.
-
Web Break
A tear in a web roll during the printing process.
-
Web Press
Cylinder printing machine in which the paper is fed from a continuous reel, as opposed to sheet fed.
-
Web Tension
The term given to the tension or pull exerted by the web press on the web roll.
-
Wet Trapping
The ability of an ink film to accept subsequent ink films.
-
Widow
A single word or two left at the end of a paragraph, or a part of a sentence ending a paragraph, which loops over to the next page and stands alone. Also, the last sentence of a paragraph which contains only one or two short words.
-
Widow
A widow occurs when the last line of text is less than half the length of the column width.
-
Wire Side
That side of the paper which lies on the wire screen side of the papermaking machine.
-
Wire Stitching Or Stapling
To fasten together sheets, signatures, or sections with wire staples. 3 methods... saddle stitching, side stitching, and stabbing.
-
Wove
A smooth paper made on finely textured wire that gives the paper a gentle patterned finish.
-
Writing Paper
Another name for bond paper.
-
Xerographic Paper
Papers made to reproduce well in copy machines and laser printers.
